
What is SD WAN and
how does it work?
Learn how to optimize your network
with your free For Dummies eBook!
Learn how to optimize your network
with your free For Dummies eBook!
Software defined wide area network (SD-WAN) is a type of computer network that enables bonding of multiple internet access resources – such as DSL, cable, cellular or any other IP transport – to provide reliable high throughput data channels.
SD-WAN abstracts connectivity options – like multiprotocol label switching (MPLS), mobile and broadband – to create a virtual enterprise wide-area network (WAN).
An SD-WAN has a virtual WAN architecture and a software-driven technology. A key element of an SD-WAN is its centralized control, so that network connections, security mechanisms, policies, application flows and general administration are separated from the associated hardware.
For security considerations, data communications between offices are typically transmitted via VPN and funneled through the main office facility. It is critical to have a high-throughput IP tunnel that is reliable for this data connection. If a branch office uses a single DSL, T1 or cable modem connection to communicate with the headquarter office, there may be insufficient throughput
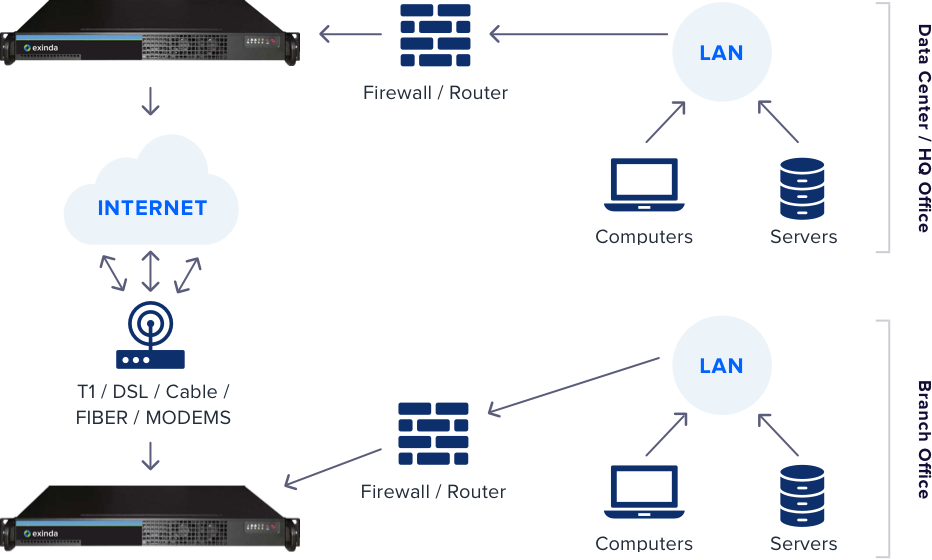
and speed – especially for uploading data from the branch office to the main office. Similarly, a single broadband line at the branch office will not provide the adequate up-time that business-critical applications demand.
SD-WAN’s architecture enables a high-speed IP communication framework between a branch office and headquarters – as well as among branch offices – even over large geographic areas. The two devices form a transparent, high-speed data tunnel between them by combining access resources on each side.
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is simply a computer network that covers a large geographical area – usually encompassing a series of Local Area Networks (LANs). The connections can be telephone systems, leased lines or satellites.
With the proliferation of cloud services based on private and public clouds – as well as services that are heavily dependent on reliable and high-performance applications – businesses are sometimes maxing out the limitations of available WAN services. Although it may be economically feasible to provide high bandwidth internet connectivity to the main office, providing the same speed connections to each branch office is prohibitively expensive. There may be many branch offices and the available internet services might be limited or costly.
A software defined wide area network is a departure from the way a WAN is typically deployed and managed. An SD-WAN is a software-based technology that overlays onto an existing network. With an SD-WAN, the physical network is separate from the logical network. It splits the network from the management plane and disconnects the traffic management and monitoring tasks from the hardware. For instance, traditional WANs can only handle so many incoming
connections to multiple cloud platforms. SD-WANs are not limited by the underlying hardware that makes up the network.
SD-WAN technology can provide fast, reliable and relatively inexpensive data connectivity between the main office or data center of business with its branches. Compared to the alternative of using a single and expensive internet line, an SD-WAN can significantly cut WAN expenses. Beyond such cost savings, businesses can get reliable, general internet access for offices through the internet connection at the main office.
Many companies are turning to software defined wide area network technology to solve a wide range of network connectivity and performance issues, and boost their business results. Benefits to organizations include:
 Save money
Save moneySD‐WAN delivers the advantages of a dependable, secure WAN service at internet prices. Broadband is more economical and flexible than expensive carrier-grade MPLS connections that typically have long provisioning times and costly contracts. With SD-WAN technology companies can use all available network connections to their full capacity without maintaining unused backup links.
 Add security
Add securitySD-WAN technology distributes security at the branch level, avoiding the limitations of data having to return to a data center for added security protections such as firewall gateways or domain name system (DNS) enforcement. SD-WANs encrypt WAN traffic as it changes locations. It segments the network, minimizing damage if a breach occurs. SD-WANs can also help IT administrators detect attacks more quickly by letting them monitor the amount and types of traffic on a network. There is added security because SD-WANs allow for the use of virtual private networks (VPNs).
 Increase agility
Increase agilitySD-WAN allows businesses to easily add or remove WAN connections – as well as combine cellular and fixed-line connections. Branches become more agile because SD-WANs allows multiple links, devices and services to coexist with the older infrastructure. With SD-WAN technology, the main office can quickly deploy WAN services to a distant site without having to send IT personnel there. Businesses can reduce deployment and configuration times with the more agile SD-WAN technology. In fact, network agility was recently cited as a key reason why business are adopting SD-WANs, according to a recent industry survey. [1]
 Simplify management
Simplify managementSD‐WAN makes deploying branch-level WAN services fast and simple. Because SD-WANs are based on a central cloud architecture, businesses find it easy to scale across the many endpoints. Companies can streamline branch infrastructure by inserting network services — whether in the cloud, branch edge or in data centers. IT staff have the ability to globally automate zero-touch deployment with a single management interface. SD-WAN offers services like WAN optimization, so fewer network appliances are needed at each location.
 Improve the user experience
Improve the user experienceBecause an SD-WAN uses a central control function to direct traffic across the WAN, it increases application performance and enhances the user experience – along with increased user productivity and reduced IT costs. SD-WANs can provide a superior cloud application performance from multiple clouds to multiple end users in multiple locations. If a link fails or there is degradation, the SD-WAN can route can dynamically route traffic between dedicated circuits and secure internet connections – without interruptions to essential applications.
 Gain better performance
Gain better performanceSD-WAN technology uses the internet to create secure, high-performance connections – removing MPLS network backhaul penalties. Business application optimization can be provided cost effectively, while greatly enhancing Software as a Service (SaaS) and other cloud-based services. Also, remote users typically experience less network latency and faster connections when using the cloud/SaaS‐based applications.
Companies are rapidly adopting software defined wide area network technology because of its many operational and financial benefits. In fact, the International Data Corporation (IDC) predicts that the SD-WAN infrastructure market will grow at a 40.4 percent compound annual growth rate, reaching $4.5 billion by 2022. [2]
SD-WANs can solve a major business problem of ensuring reliable internet connectivity. Without robust connectivity, a business may face disruptions caused by link failures, network latency or WAN blackouts. These disruptions can be costly. Gartner estimates [3] network downtime may cost up to $5,600 per minute, or more than $300,000 per hour.
In spite of all the advantages, SD-WAN control and management across multiple locations can still be a significant challenge for businesses with IT resource limitations. Many organizations are turning to third-party SD-WAN providers for SD-WAN management software solutions. One example is the Exinda SD-WAN software from SD-WAN vendor, GFI Software.
With Exinda SD-WAN, you can combine and manage up to twelve internet connections into a single, ultra-high-speed line through a bonding tunnel. With the overlay tunnel technology of Exinda SD-WAN, the application flows can be kept alive even during WAN blackouts or brownouts, providing seamless session continuity.

Exinda features include:
Another feature is Exinda’s intelligent WAN automation. The overlay tunnels leverage advanced algorithms to monitor, remember, learn and react to a business’ network traffic in real-time and on the packet level. Services such as live video, VOIP, chat applications, file transfers or any other types of specific application flows are mapped onto corresponding overlay tunnels.
Connecting Branch and Central Offices Cost-effectively and Reliably
See how you can take advantage of low-cost transport technologies and carrier diversity to enable fast and reliable connectivity.
Introducing Exinda SD-WAN
Watch this short video to see how SD-WAN technology can help you achieve exceptional application performance on your network.
1 The Future of SD-WANs – Peril or Promise? Cato Networks. April 2017.
2 SD-WAN Infrastructure Market Poised to Reach $4.5 Billion in 2022, According to IDC. Press release August 7, 2018.
3 The Cost of Downtime. Andrew Lerner. Blog. July 16, 2014.

